What are AI Agents?
AI agents are autonomous software programs that perceive their environment through sensors and act on it using actuators. They operate independently without human intervention and execute tasks by leveraging advanced technologies such as machine learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), large language models (LLMs), or Foundation Models (FMs).
AI agents excel at solving complex problems by decomposing queries, planning task sequences, and employing a reasoning process akin to human thought. They can handle ambiguous questions and utilize various tools, such as APIs, programs, and web searches, to execute tasks and find solutions effectively.
How do AI Agents Work?
AI is a rational agent, and a human can also be a rational agent, as can an enterprise, a machine, or software. An AI agent considers past and present relevant factors to arrive at an optimal, desirable outcome.
Before proceeding, it’s important to understand sensors, effectors, and actuators.
- Sensor: An electronic device that picks up on environmental changes and sends that information to other electronic devices. Through sensors, an agent can observe its surroundings.
- Actuators: Parts of machines that turn energy into action. Actuators are limited to the movement and control of the AI system. Electric motors, gears, rails, and other mechanisms can all function as actuators.
- Effectors: Devices that have an impact on the environment. Effectors include legs, wheels, arms, fingers, fins, wings, and display screens.
Let’s look at some of the features, benefits, and architecture of AI agents in this article:
AI Agents Key Features
- Autonomous Task Execution – AI Agents can perform tasks end-to-end without human intervention, leveraging advanced machine learning and large language models. For example, they can process a customer query, identify the required information from multiple systems, execute relevant actions (e.g., update records or place orders), and confirm the outcome autonomously.
- Decision-Making Abilities – Intelligent Agents analyze available data, weigh options, and make informed decisions to accomplish their goals. These decisions may involve selecting the optimal path for task completion, prioritizing actions, or resolving conflicts based on programmed or learned logic.
- Contextual Understanding – By interpreting the context of user inputs, ongoing conversations, or task history, AI Agents understand nuances, intent, and dependencies. This enables them to provide relevant and personalized responses or solutions, even in complex scenarios.
- Dynamic Learning – AI systems continuously learn from new data, user interactions, and feedback. This allows them to improve over time, adapt to evolving user needs, and refine their processes to become more efficient and accurate.
- Multi-modal Capabilities – System of AI Agents can interact using different forms of communication, such as text, voice, images, and even video. Multimodal LLMs capabilities enable seamless integration across communication channels, enhancing accessibility and user experience.
- Real-Time Adaptation – AI can adjust its behavior and responses based on real-time changes in data, user inputs, or environmental factors. For example, they can modify their mid-task approach if new information becomes available or the context shifts.
- Predictive Abilities – Using historical data and pattern recognition, AI Agents can anticipate user needs, predict outcomes, or identify potential issues before they occur. For instance, they might proactively suggest actions or flag anomalies for review.
- Transparency – AI Agents provide visibility into their decision-making processes, task progress, and outcomes. This fosters trust by allowing users to understand why the generative AI made a specific choice or took a particular action.
- Tool Use – Agents can leverage external tools, APIs, and systems to enhance their capabilities. For instance, they may access enterprise databases, use productivity software, or interact with analytics platforms to complete tasks effectively.
- Interactivity with Digital Interfaces – AI Agents can seamlessly navigate and interact with digital interfaces like web applications, portals, or software tools. They mimic human interactions, such as filling out forms or navigating menus, to accomplish goals within existing systems.
Key Benefits of AI Agents
- Enhancing Productivity and Efficiency: It automates repetitive and time consuming tasks like data entry, ticket resolution, and process workflow. They orchestrate across multiple systems dynamically so employees can focus on strategic, creative, or decision making tasks. This means faster task completion, reduced bottlenecks, and improved operational efficiency across teams and departments.
- Cost Reduction and Improved ROI: By automating routine and high volume processes, AI Agents reduce dependency on manual labor, saving time and resources. They also minimize errors and rework, improving overall operational accuracy. These efficiencies translate to measurable cost savings and better utilization of human and technological resources, resulting in higher ROI with AI on technology investments.
- Enabling Informed Decision-Making: AI Agents analyze vast amounts of data in real-time and provide actionable insights and recommendations. They use predictive analytics and contextual understanding to identify trends, forecast outcomes, and assist in strategic planning. This enables leaders to make informed, proactive decisions and mitigate risks and seize opportunities faster.
- Enhancing Customer Experiences: System of AI agents ensure seamless interactions by delivering instant, personalized and accurate answers to customer queries. Integrating AI agents with multiple channels like chatbots, email and voice assistants means customers can engage anytime, anywhere. With capabilities like contextual understanding, proactive assistance and continuous learning, they improve first contact resolution rates, reduce wait times and boost customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Scalability and Agility: Scaling agentic AI handles increased workloads, making it perfect for organizations growing or experiencing seasonal spikes in demand. They adapt to changing business needs by learning new tasks and incorporating new tools or systems, so they’re flexible and have long-term value
- Improved Employee Experience: By handling mundane and repetitive tasks, AI Agents take the workload off employees, reduce burnout and increase job satisfaction. They also act as intelligent assistants, giving employees quick access to information, resources, and insights so they can work better and more efficiently.
- Consistency and Reliability: Unlike humans, AI Agents work 24/7 with no fatigue. They execute tasks without error, so consistency and accuracy are maintained in every interaction or process they manage.
- Future-Proofing Organizations: With their ability to integrate with modern systems, use large language models (LLMs), and continuous learning AI Agents future future-proof your organization for an AI driven world.
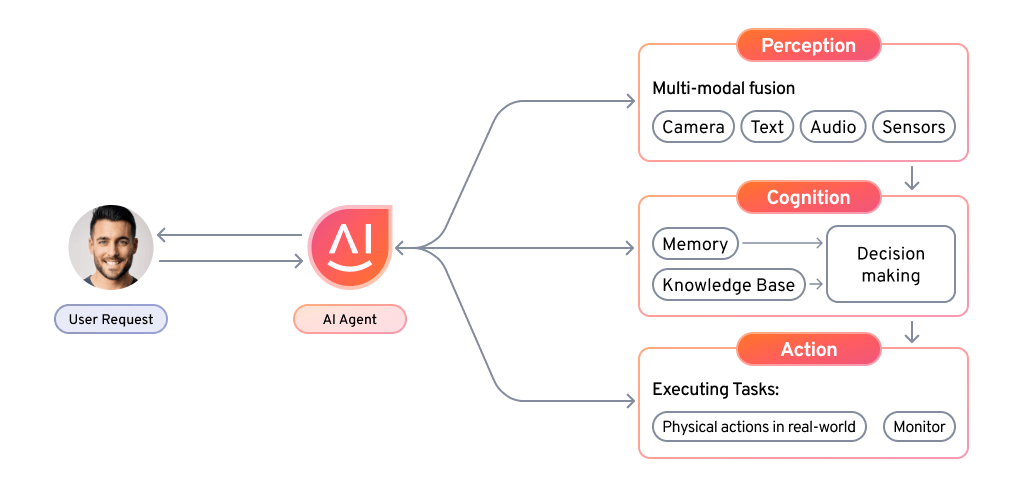
Architectural Components of AI Agents
Agentic systems have several interconnected components that work together to enable intelligent behavior. Each element plays a crucial role in the overall functioning of the AI system, and they must interact seamlessly to achieve desired outcomes. Let’s explore each of these components in more detail.
Perception Module
Sensory input gathers data, feature extraction processes it, and object recognition identifies key elements using AI techniques.
Cognitive Module
Goal representation defines objectives, planning maps out strategies, and decision-making selects the best action to achieve results.
Action Module
Actuators enable actions, while execution carries them out to interact with the environment.
Learning Module
Reinforcement learning learns through rewards, supervised learning from labeled data, and unsupervised learning finds patterns in unlabeled data.
Types of AI Agents
To move from the abstract to specifics, let’s examine the actual types of AI agent functions in their hierarchy. AI agents can be categorized based on their capabilities, autonomy, and interaction with their environment. The more deeply a user understands them, the easier it is to select the right AI agent for their purposes. Here is a sampling of well-known AI agents:
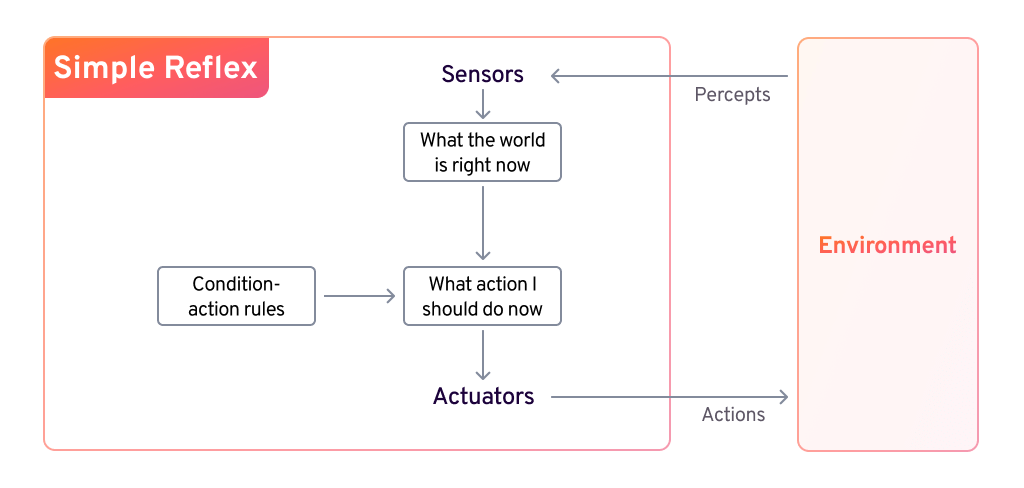
Simple Reflex Agent
A simple reflex agent reacts to its current environment using predefined condition-action rules, without memory or learning. It works best in fully observable environments but struggles in complex or dynamic ones. Lacking adaptability, it cannot handle unstructured scenarios and requires manual rule updates for changes. While useful for basic tasks, it falls short in situations requiring reasoning or long-term learning.
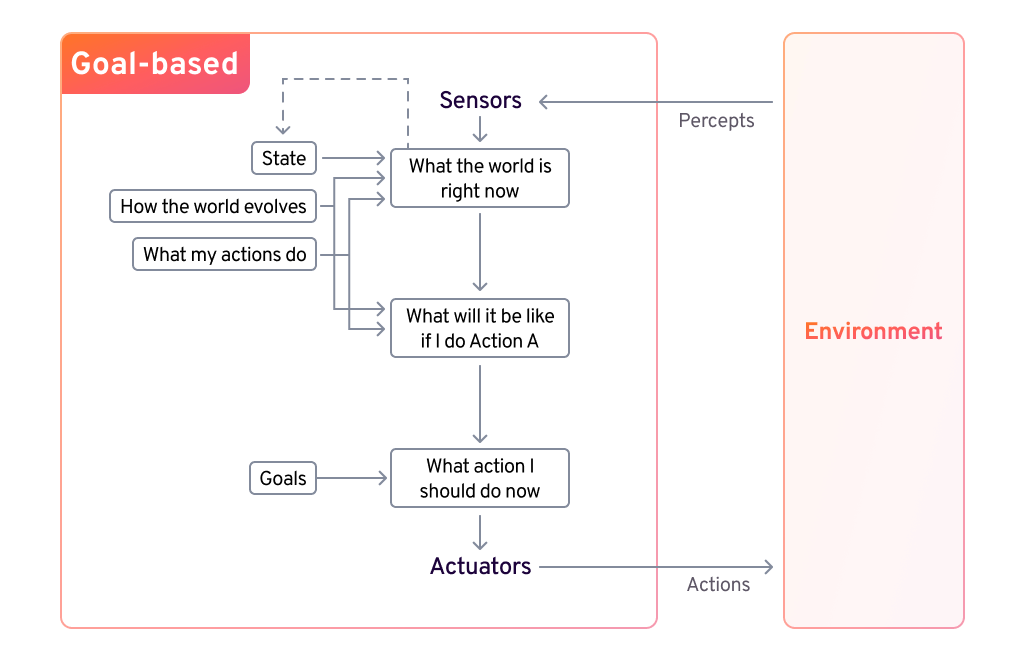
Goal-Based Agents
Goal-based agents make decisions by considering future outcomes and selecting actions that bring them closer to their objective. They use search, planning, and adaptable decision-making, allowing for flexibility in complex tasks like navigation and gameplay.
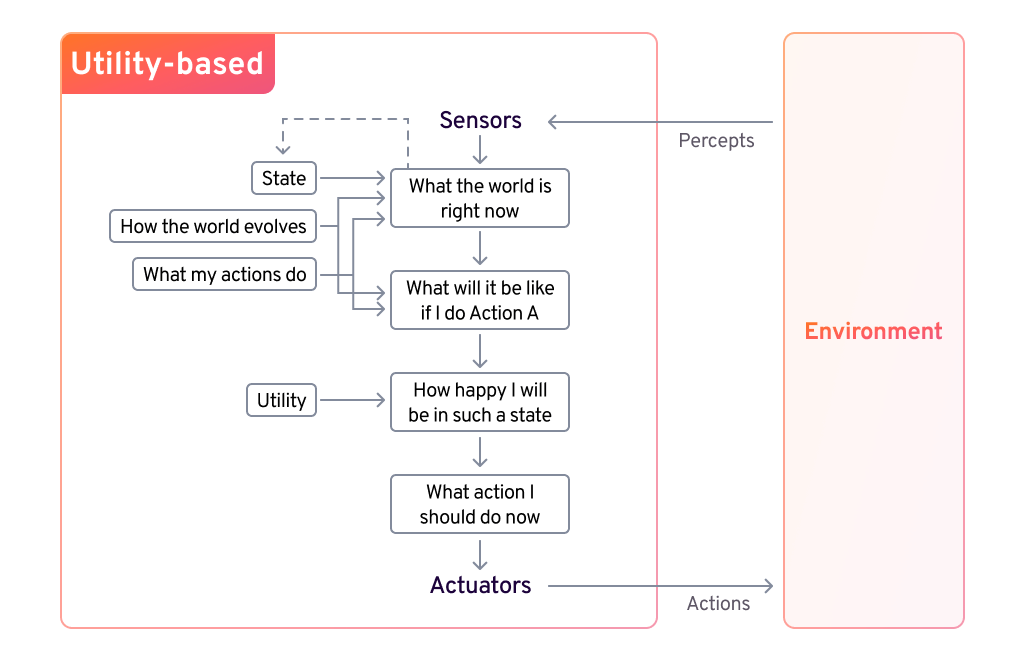
Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents optimize decision-making by evaluating actions using a utility function to maximize performance. They consider factors like cost, speed, and safety, selecting the most beneficial path in complex or uncertain environments.
Autonomous Agents Learning
Learning agents adapt and improve through experience, optimizing strategies over time. They consist of a learning element (adapts to data), a critic (provides feedback), a performance element (selects actions), and a problem generator (explores new possibilities), making them ideal for dynamic environments like personalized marketing.
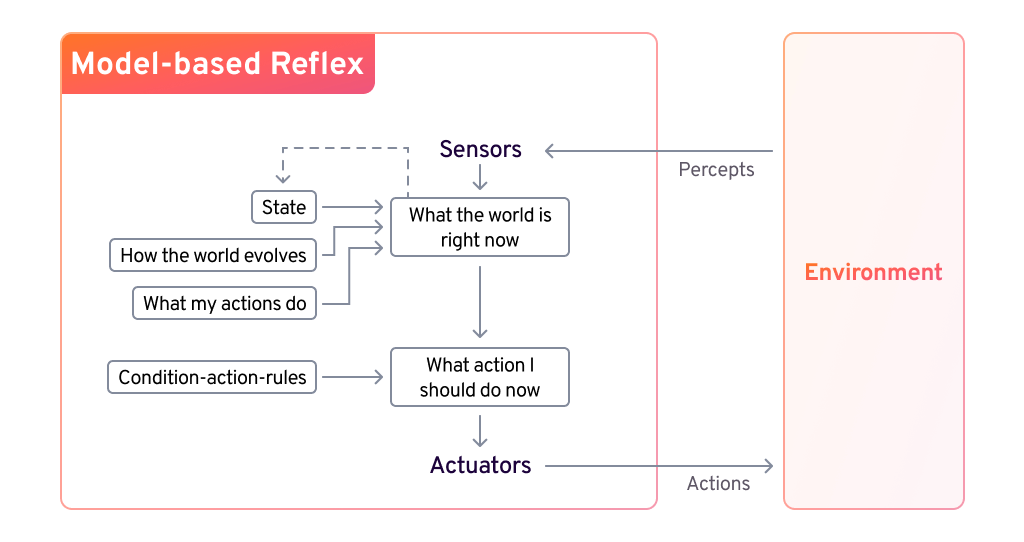
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Model-based agents use an internal world model to infer missing information and handle partially observable environments. They update their state based on percept history, tracking changes in the world and how their actions impact it.
Autonomous Learning Agents
Learning agents adapt and improve through experience, optimizing strategies over time. They consist of a learning element (adapts to data), a critic (provides feedback), a performance element (selects actions), and a problem generator (explores new possibilities), making them ideal for dynamic environments.

Multi-Agent System
Multi-agent systems (MAS) consist of autonomous or semi-autonomous agents that interact and collaborate to achieve goals. Used in areas like robotics, autonomous driving, and trading, MAS improves efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances flexibility. They can be homogeneous (identical agents) or heterogeneous (agents with different capabilities and goals).
Hierarchical Agents
Hierarchical agents operate in multi-layered structures where high-level agents set goals and low-level agents execute tasks. This approach enhances efficiency in complex systems by breaking down tasks and ensuring organized decision-making.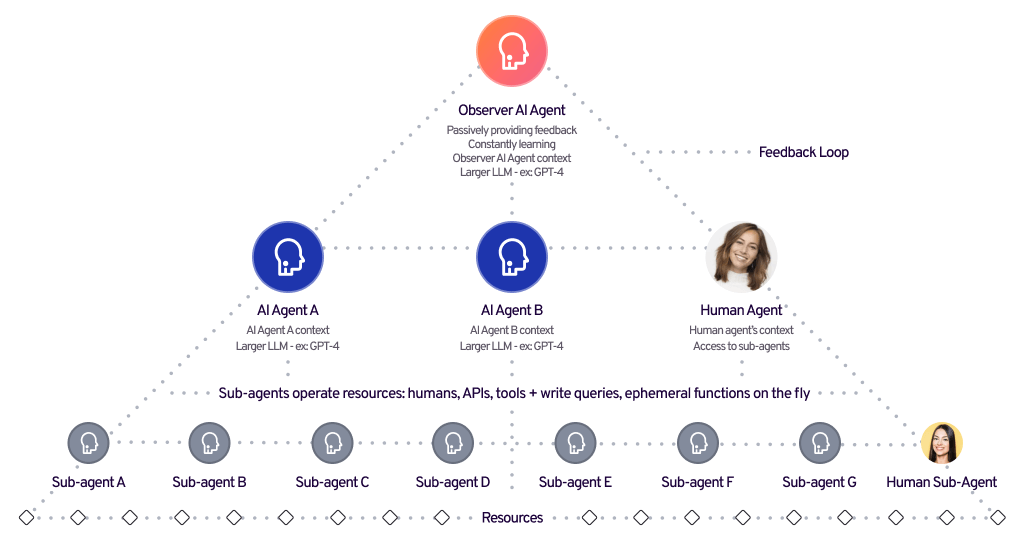
Key Characteristics:
- High-Level Agents: Define goals, set constraints, and guide the system, ensuring strategic alignment.
- Low-Level Agents: Execute specific tasks based on instructions from high-level agents.
- Task Decomposition: Large tasks are broken into smaller, manageable sub-tasks for efficiency.
- Scalability & Flexibility: New agents or layers can be added to adapt to evolving environments.
- Efficiency & Adaptability: Optimizes resources, reduces redundancy, and adjusts to changing conditions.
- Autonomous Decision-Making: Low-level agents make real-time decisions based on local conditions.
Deploying AI Agents
AI agents have immense potential to revolutionize workflows by agentic workflows, enhance productivity, and improve decision-making. However, deploying AI agents requires careful planning, ethical considerations, and adherence to best practices to ensure successful implementation. Below, we explore the key challenges, considerations, and actionable tips for deploying AI agents effectively.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns:
- Challenge: AI agents often require access to sensitive data to function effectively, raising concerns about user privacy, data security, and compliance with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA. Ethical concerns, such as bias in decision-making or unintended consequences, can also emerge.
- Mitigation: Ensure transparency in data collection and usage, enforce strict data protection protocols, and implement AI models that reduce bias through diverse training datasets and regular audits.
2. Technical Complexities and Resource Limitations:
- Challenge: AI agent deployment demands significant computational resources, integration with existing systems, and skilled personnel. Technical issues like latency, scalability, and model interpretability can hinder implementation.
- Mitigation: Invest in robust infrastructure, cloud-based solutions, and skilled teams while collaborating with technology partners to streamline the deployment process.
3. Adaptability and Scalability:
- Challenge: AI agents must be adaptable to evolving business needs and capable of scaling across different departments or locations. Over-reliance on static models can limit long-term effectiveness.
- Mitigation: Implement flexible, modular architectures and continuously train AI models to ensure scalability and relevance in dynamic environments.
4. Integration with Legacy Systems:
- Challenge: Many organizations have existing legacy systems that lack compatibility with modern AI agents, making integration challenging.
- Mitigation: Use middleware solutions or APIs to bridge the gap between legacy systems and AI agents, ensuring seamless data flow and functionality.
Best Practices for AI Agent Implementation
- Start with a Clear Objective: Define specific, measurable goals for the AI agent, such as reducing response times, automating specific tasks, or improving decision accuracy. This helps align the deployment with business needs.
- Develop a Pilot Program: Begin with a small-scale implementation to identify potential challenges, gather feedback, and refine the AI agent before scaling across the organization.
- Prioritize Data Quality: High-quality, relevant data is critical for AI agents to function effectively. Invest in data cleaning, labeling, and enrichment processes to maximize model performance.
- Ensure Transparency and Explainability: Deploy AI agents with built-in explainability features to make their decision-making process transparent. This fosters trust among stakeholders and enables regulatory compliance.
- Train and Upskill Teams: Equip employees with the necessary skills to interact with and manage AI agents. Training programs can help teams understand how to leverage AI agents effectively.
- Monitor and Optimize Performance: Regularly evaluate the AI agent’s performance using KPIs and user feedback. AI agent evaluation is important to retrain and fine-tune models, ensuring continuous improvement.
- Plan for Long-Term Maintenance: AI agent deployment is an ongoing process. Allocate resources for updates, monitoring, and addressing emerging challenges to ensure sustained success.
- Foster Stakeholder Engagement: Communicate the benefits of AI agents to all stakeholders, addressing potential concerns early on and fostering a culture of collaboration and innovation.
Now, let’s look at some of the best practices for successful AI Agent deployment.
Tips for Successful AI Agent Deployment
- Define Specific Use Cases: Start with targeted use cases where AI agents can provide immediate value, such as automating repetitive tasks or improving customer interactions.
- Involve Stakeholders Early: Engage teams from across the organization, including IT, legal, and operations, to align deployment efforts with business priorities.
- Focus on Security: Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and prevent breaches.
- Leverage Pre-Trained Models: Use pre-trained models to reduce development time and cost while ensuring high performance in standard tasks.
- Integrate with Existing Systems: Use APIs, middleware, or cloud platforms to ensure seamless integration with current technologies and workflows.
- Establish Clear Metrics: Track metrics such as task completion rates, user satisfaction, and cost savings to measure success.
- Iterate Based on Feedback: Gather insights from users and stakeholders to refine AI agent capabilities and address pain points.
- Stay Compliant: Regularly review deployment practices to ensure compliance with local and international regulations, such as data privacy laws.
Best Practices for AI Agent Implementation
- Start with Clear Objectives – Define measurable goals like automating tasks, improving decision accuracy, or enhancing response times to align AI deployment with business needs.
- Pilot Before Scaling – Launch a small-scale implementation to identify challenges, gather feedback, and refine AI agents before a full rollout.
- Ensure High-Quality Data – AI performance depends on clean, labeled, and enriched data, making data quality a top priority.
- Emphasize Transparency & Security – Implement explainability features to build trust and ensure compliance while securing sensitive data against breaches.
- Train & Engage Stakeholders – Equip teams with AI management skills, involve IT, legal, and operations early, and foster collaboration for smoother adoption.
- Monitor, Optimize & Iterate – Track KPIs, collect user feedback, and continuously refine AI models to maintain performance and adaptability.
- Plan for Long-Term Maintenance – Allocate resources for updates, compliance reviews, and integration with evolving enterprise systems to sustain success.
AI Agent Integration
AI agents can be integrated into an existing system using various programming languages, including Python, Java, and C++. These languages offer robust libraries and frameworks that facilitate the development of AI functionalities. Once developed, AI agents can be integrated into a wide range of applications, such as chatbots, virtual assistants, and expert systems, to enhance their capabilities and user interactions.
Building a Robust AI Agent Memory System
A robust AI agent memory system is essential for developing advanced AI agents capable of performing complex tasks and interacting effectively with their environment. Such a memory system should exhibit several key characteristics:
- Multimodality: The ability to process and store information from various sources, such as text, images, and sensor data, enabling the agent to understand and respond to diverse inputs.
- Operationality: Ensuring that the memory system is efficient and reliable, allowing the agent to retrieve and use stored information quickly and accurately during task execution.
- Sharability: Facilitating the sharing of information between multiple agents, enhancing collaboration and collective problem-solving capabilities.
By incorporating these characteristics, a robust memory system empowers AI agents to handle advanced tasks, adapt to new situations, and collaborate effectively with other agents, driving significant improvements in performance and functionality.
AI Agents' Impact Across Industries
AI agents are versatile enough to add value across nearly every modern industry, bringing revolutionary advances to business sectors. Each sector leverages these agents in unique ways. Here’s a look at how they are being utilized in different business sectors:
Finance Sector
AI agents perform multiple functions that include optimizing investment strategies and managing large portfolios. They use real-time analysis to autonomously make trading decisions, based on both predefined strategies and real-time, dynamic market conditions, providing clients with improved financial returns. AI agents constantly consume market data and economic indicators to assess portfolio risks and calculate the impact of fast-breaking financial events with dazzling accuracy.
Energy Sector
Energy and power benefit from the ability of AI agents to manage and optimize energy distribution and consumption. Agents can calculate and predict demand patterns, optimize grid operations, and even proactively detect potential system failures in time to minimize or avoid outages, loss, and damage. AI agents constantly analyze data from a multitude of sensors and systems, which helps accurately balance energy supply and demand—moving toward sustainability, intelligent economic strategy, and environmentally beneficial energy management.
Transportation and Logistics
One high-impact application of AI agents is developing self-driving cars that can safely navigate complex intelligent systems in urban environments and interact with other road users. AI agents allow these vehicles to process data from sensors (LIDAR, cameras, radar) and make real-time driving decisions. They control a vehicle’s acceleration, braking, and steering to navigate through traffic and have successfully logged billions of miles safely and efficiently.
Health Sector
AI agents are making history daily in healthcare, assisting in diagnosing diseases and recommending personalized treatment plans based on huge volumes of medical data. IBM Watson for Oncology, for example, uses AI agents to analyze medical records, research papers, and clinical guidelines for evidence-based treatment recommendations. AI agents aggregate and study data from electronic health records (EHRs), medical literature, and clinical trial results. They employ NLP to interpret unstructured medical texts and extract relevant information that humans could miss. AI agents can suggest potential diagnoses and treatment options based on up-to-the-minute medical evidence and patient-specific factors, helping develop effective, personalized treatment plans and improving patient outcomes.
Customer Service
AI agents have revolutionized customer service by providing instant, accurate, and personalized responses to customer inquiries. Companies in all verticals can now easily and cost-efficiently help customers with countless tasks and information needs. An AI assistant can use Natural Language Understanding (NLU) to comprehend and act upon customer queries expressed in common, “natural” talk.
Using machine learning, the assistant comprehends relevant information to improve responses and provide personalized assistance. AI agents can integrate with a company’s other agents or existing systems to access account information, perform transactions, and provide personalized advice. Today, AI agents handle millions of customer interactions, improving response times, reducing workload for human agents, and transforming the customer experience profoundly.
How can Aisera help with Agentic AI and AI Agents?
Aisera’s Agentic AI platform provides enterprises with out-of-the-box AI solutions, seamlessly integrating with existing systems for a smooth transition to advanced AI agents. Its specialized agents leverage dynamic learning, real-time decision-making, and automation to boost efficiency and user experiences.
With 100+ pre-built integrations, Aisera accelerates deployment and adapts to enterprise needs across IT, HR, Security, and more. Additionally, its domain-specific language models deliver precise, context-aware responses tailored for industries like Pharma, Banking, and Insurance, ensuring accuracy and relevance in AI-driven interactions.
The Future of AI Agents
The field of AI agents is rapidly evolving. Combining deep learning with reinforcement learning has led to breakthroughs in creating more capable and sophisticated AI agents. Their future is defined by greater autonomy, improved intelligence, and seamless integration into human and machine ecosystems.
One emerging idea is the development of AI Agents with a form of artificial general intelligence (AGI), enabling them to handle tasks across any context with universal adaptability and autonomy. However, practical AGI is still a distant goal far from being realized. Companies aren’t ready to let AI agents autonomously create systems or policies using general intelligence.
Conclusion
AI Agents are transforming problem-solving, automation, and decision-making by combining machine learning, large language models, and real-time adaptability. They enhance productivity, improve customer experiences, and enable seamless human-AI collaboration, shaping the future of work and innovation.
Enterprises adopting AI Agents should focus on strategic implementation, ethical considerations, and alignment with business goals to unlock their full potential. Aisera is leading this revolution with an enterprise-grade, scalable platform that seamlessly integrates with existing systems, driving meaningful change and innovation.
Book a custom AI demo to experience the power of Agentic AI in action.