Introduction to AI Agents, Examples, and Their Impact
AI agents are a big leap forward in agentic AI in many areas. They can do tasks on their own without a human to help. They can understand data, make good decisions and take action. That’s how we work and how businesses operate.
These intelligent agents are versatile and can be applied in many areas, including robotics, finance, healthcare, and customer service. Automating complex tasks and learning from experience make them efficient and effective across industries.
AI Agents and How They Work
AI agents are autonomous software programs that perceive their environment through sensors and act on it using actuators, running independently without human intervention by using advanced technologies like machine learning and large language models (LLMs).
They are great at solving complex problems by breaking down queries, planning task sequences, and using a reasoning process to handle ambiguity, often using tools like web searches and APIs to find a solution.
From the AI assistants on our phones to the complex systems managing financial trades, these agents are already a game changer and in this article, we’ll show you 24 real-world examples to see how they work and the impact they’re having across industries.
Types of AI Agents with with Examples
AI agents come in different levels of autonomy, capability, and interaction. Understanding what AI agents are and how they work helps us choose the right agent for a certain domain or industry. These agents are categorized based on their perception of the environment, decision-making, and action. Here are some of the most common types of AI agents.
1. Simple Reflex Agents
- Description: Reacts to the current environment using predefined condition-action rules. Lacks memory and adaptability.
- Pros: Fast, predictable, inexpensive.
- Cons: No memory, brittle in noisy settings.
- Example: Threshold alerts, thermostats.
2. Goal-Based Agents
- Description: Makes decisions by evaluating future outcomes and selecting actions that achieve specific goals.
- Pros: Flexible, better at multi-step tasks.
- Cons: Goal specification and constraints must be clear.
- Example: Route planners, treatment planners.
3. Utility-Based Agents
- Description: Uses a utility function to evaluate actions and optimize performance based on factors like cost, speed, and safety.
- Pros: Handles competing objectives.
- Cons: Utility design and calibration can be hard.
- Example: Self-Driving Cars (Tesla Autopilot) – Chooses the safest and most efficient driving maneuvers by considering factors like road conditions and vehicle speed.
4. Model-Based Reflex Agents
- Description: Uses an internal world model to infer missing information and operate in partially observable environments.
- Pros: Works in partially observable settings, more robust than pure reflex.
- Cons: Requires model design and upkeep.
- Example: Chatbots with Context Awareness (e.g., Alexa, Google Assistant) – Maintains memory of previous interactions to provide relevant responses.
5. Autonomous Learning Agents
- Description: Improves performance through learning, adapts to new data, and refines decision-making over time.
- Pros: Adapt to drift, reduce manual tuning.
- Cons: Data quality, bias, and safety risks if feedback is noisy.
- Example: Recommendation Systems (Netflix, Spotify) – Learns user preferences and suggests personalized content based on viewing or listening history.
6. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
- Description: Multi-agent system is a network of multiple agents working together to achieve a common goal, enhancing efficiency and flexibility.
- Pros: Scales across roles, enables specialization and redundancy.
- Cons: Coordination overhead, conflict resolution needed.
- Example: Stock Market Trading Algorithms – Automated trading bots analyze market trends and execute trades collaboratively to maximize profits.
7. Hierarchical Agents
- Description: Operate in a multi-layered structure, where high-level agents define goals, and low-level agents execute tasks.
- Pros: Clear delegation, easier debugging of complex tasks.
- Cons: Failure propagation across levels if not isolated.
- Example: Supply Chain Management Systems (Amazon’s Logistics AI) – High-level AI manages inventory distribution, while lower-level AI optimizes warehouse picking and packing operations.
8. Embodied Agents
- Description: Software controlling physical systems.
- Pros: Real world impact, end-to-end automation.
- Cons: Safety, latency, hardware costs.
- Example: Mobile robots, autonomous vehicles, drones.
9. Tool-Using LLM Agents
- Description: LLM plans and calls external tools through functions.
- Pros: Broad capability with minimal custom code.
- Cons: Tool reliability and schema drift must be managed.
- Example: Booking, research, report generation, code changes.
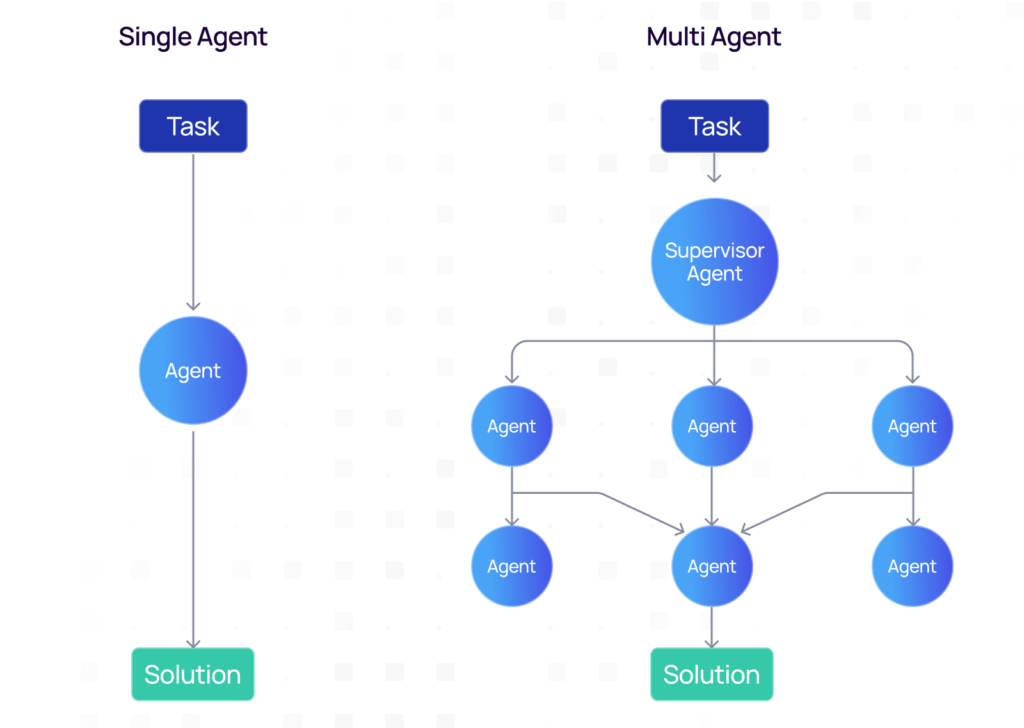
The illustrated images depict a simple schematic of a single-agent system vs. a multi-agent system.
24 AI Agents Examples and Use Cases
Building AI agents to leverage them in any industry is no longer theoretical; they are actively deployed across every major industry, streamlining operations and creating new possibilities. Here are over 20 practical examples of AI agents at work.
AI Agents Examples in Finance Industry
AI in fintech plays a crucial role in financial services. similar to advancements like generative AI in banking, AI agents are changing finance. They help with fraud detection, risk assessment, and trading. These tools use big data and learning algorithms to improve security, accuracy, and reduce business operation costs.
8. Fraud Detection
AI agents can check up to 5,000 transaction details in milliseconds, that’s way faster than humans who look at 20-30 points. They look for unusual patterns to spot fraud quickly and accurately.
Artificial intelligence systems are scalable and can handle thousands of transactions per second. That’s how they are key in stopping fraud. They protect people and banks from scams.
9. Risk Assessment
AI agents use predictive analytics and machine learning to do risk checks. They do stress tests and scenarios to identify risks humans might miss.
AI agents can work independently, learning and planning. For example, JP Morgan’s COiN platform uses AI to check legal documents. This used to take lawyers thousands of hours, now it’s much faster and more accurate.
Utility-based agents play a big role in financial risk assessment. They evaluate multiple factors to find the best course of action. These agents weigh potential risks against expected returns, ensuring optimal investment and lending decisions.
For example, JP Morgan’s COiN platform uses AI to assess contract risks, prioritizing actions that maximize financial security while minimizing exposure.
10. Algorithmic Trading
AI agents are changing trading by using fast algorithms. They can make thousands of trades per second, using learning strategies based on market data to make better trades.
AI helps high-frequency trading firms make better trades faster. Adding AI to blockchain and quantum computing makes trading even more advanced.
AI agents are making finance operations more efficient, precise, and safe. Bank of America and JPMorgan Chase are leaders in showing how AI agents can make a big impact in the financial industries.

AI Agents Examples for Customer Support
AI agents are changing customer support with 24/7 help and quick answers. Advanced models of enterprise AI chatbots and AI virtual assistants make it easier to handle customer questions. They assess inputs and know when to escalate complex issues to a human agent for resolution so human experts handle situations that require nuance or intervention.
20. Instant Response and 24/7 Support
AI customer service works 24/7 providing fast help to customers. Customers are happier and more loyal. 72% of people stay with companies that serve them fast.
AI can handle many questions, reducing wait times and increasing productivity by 14%. The city of Amarillo, Texas, uses AI like Emma for 24/7 support in many languages.
21. Escalating Complex Customer Issues
AI agents can solve simple problems but know when to send tricky ones to humans. They look for signs that a problem needs a human touch and make sure complex issues get the right attention.
AI also shares knowledge articles that can solve problems before they become too big. Companies like ServiceNow use AI to improve their services and lighten the load on their teams. This is seen in 79% of IT leaders’ reports.
Even with the cost of new technology, 83% of leaders will invest more in AI. They think it makes customer support better.
Here’s the table on the impact and benefits of AI agents in customer support:
AI Agents Examples in HR, Sales, and Marketing
Agentic AI in HR is popping up, similar to sales and marketing workflows, where repetitive but critical tasks eat up hours. By automating these processes, agents save costs, increase efficiency, and let human teams focus on higher-value work.
17. HR
AI agents for HR streamline employee lifecycle management.
- Onboarding: New hires get automated checklists, training modules and system access in hours not days.
- Access Provisioning: Agents talk to identity management systems to grant or revoke access as roles change, reducing IT bottlenecks.
- Policy Q&A: Virtual HR assistants answer questions about leave policies, payroll or benefits instantly, reducing helpdesk volumes.
- Benefits Explanations: Natural language agents give tailored guidance on health plans and retirement programs, improving employee satisfaction.
- Interview Scheduling: Coordinating candidate interviews is automated with calendar integrations, cutting recruiter workload by up to 40%.
18. Sales
In sales, AI agents drive pipeline growth and deal velocity.
- Prospecting: Agents scan public data, enrich leads with firmographics and surface high intent prospects.
- Lead Enrichment: Contact records are updated automatically with titles, company size and engagement scores.
- Sequence Writing: AI agents write personalized outreach messages, aligning tone and content to industry or persona.
- Meeting Scheduling: Calendar agents remove back and forth emails by booking mutually available slots.
- CRM Hygiene: Agents log calls, update opportunities and flag stalled deals, so sales teams always work with clean data.
19. Marketing
Marketing teams use AI agents to accelerate campaign creation and optimize spend.
- Brief Creation: Agents summarize goals, target audience and creative direction into actionable briefs.
- Campaign Setup: Integration with ad platforms allows agents to set up campaigns across multiple channels.
- Audience Selection: Agents identify and segment audiences by demographics, behavior or engagement history.
- Message Testing: A/B tests are launched and analyzed automatically, with recommendations for the best-performing copy.
- Post-Campaign Analysis: Agents generate reports with UTM tracking, highlighting ROI, cost per lead and recommendations for future campaigns.
AI Agents Examples in Healthcare
1. Cost Saving and Efficiency
Industry leaders have proven the ROI of AI, particularly AI agents, have reduced operational costs in healthcare, making it more efficient and improving patient care. They could save the US healthcare system up to $150 billion annually. Examples include tools that help doctors diagnose and treat patients and systems that make scheduling appointments easier.
2. Goal-Based AI in Treatment Planning
Goal-based agents play a crucial role in healthcare by identifying the best treatment plans based on patient history, symptoms, and medical guidelines. These agents use structured goals—such as minimizing diagnosis time or optimizing treatment success rates—to make decisions. For instance, AI-powered systems can recommend the most effective therapy for cancer patients based on survival probability and side effect risks.
3. AI’s Accuracy in Medical Diagnoses
AI is very accurate in medical fields. For example, an AI analysed chest X-rays for tuberculosis with 98% accuracy, beating human radiologists. It did it in seconds, compared to 4 minutes for humans.
4. NLP for Improved Patient Interaction
Natural language processing (NLP) enables AI agents to understand and process human language conversationally, allowing for more personalized and compelling user experiences.
5. AI in Healthcare Administration and Cost Reduction
AI agents help reduce the workload in healthcare by automating tasks. They can cut administrative costs by up to 30% and improve revenue cycle management. Automated tools in RCM can flag errors and speed up payment processes.
6. AI Ensuring Compliance and Data Security
AI agents also help with following rules like HIPAA compliance. They keep patient data safe and private. Automated tools can quickly check if prior authorization is needed, a task that used to take hours.
7. Growing Patient Trust in AI Health Assistants
A Deloitte survey found that 62% of patients are okay with AI health assistants answering simple questions. This shows that people are starting to trust AI for their care. AI agents help guide patients and monitor their health, making care more precise and timely.
By using AI agents, healthcare providers can meet patient needs better. They ensure patients get the proper tests and treatments based on their history and best practices.

AI Agents Examples in Manufacturing and Production
In manufacturing and production, AI agents are making big progress. They predict and schedule maintenance, improve quality control, and enhance production. AI agent technologies increase productivity, safety, and reduce costs and downtime.
Hierarchical AI agents are key in managing complex systems across various industries, such as warehouses, manufacturing, and air traffic control. This multi-layered approach involves high-level agents overseeing broader tasks and allocating resources, while lower-level agents focus on specific functions.
AI agents are perfect for industrial settings. They help with predictive maintenance by keeping an eye on equipment, which can reduce downtime by up to 30% and keep operations running with fewer stops.
8. Predictive Maintenance
AI agents are key in predictive maintenance. They analyze sensor data to guess when equipment will need fixing. For example, in energy, AI agents can improve grid management by 20%, saving money.
Model-based reflex agents play a big role in predictive maintenance. They continuously monitor sensor data and compare it against an internal model of equipment behavior. Unlike simple reflex agents that react to immediate changes, these agents use historical data and learned patterns to anticipate failures before they occur.
For example, in energy grid management, AI agents using model-based reflex mechanisms can predict potential failures with 95% accuracy, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
This avoids unplanned stops which can be costly and time-wasting. AI agents prevent these problems.
11. Quality Control
AI agents also improve quality control. They monitor production to ensure everything follows standards. For example, in the chemical industry, AI agents reduce quality failures by 30%. This saves money, ensures top-notch products and reduces waste.
12. Optimizing Production Processes
Artificial Intelligence agents improve production by optimizing how different parts work together. This can increase production by up to 25% without sacrificing quality. AI agents like GraphRAG help by analyzing data in real-time.
AI agents can help operate supply chains more efficiently. AI agents can save companies up to 40% on labor costs. This leads to a 15% increase in efficiency. Using AI smartly gives manufacturers an edge.
AI Agents Examples in E-commerce
E-commerce has changed a lot with AI agents. They do complex tasks to improve customer interaction and service delivery and increase sales. This includes placing orders, providing personalized advice and automating customer service. These changes make things run smoother and make customers happy.
13. Order Placement and Tracking
Examples of AI agents in order tracking show how they make things easier. Big names like Google and Salesforce use AI for tasks like scheduling and transactions. For example, OpenAI’s Operator can order stuff on Etsy and book campsites on Hipcamp at the same time.
This makes buying online smoother and keeps customers updated. It improves their shopping experience.
14. Personalized Recommendations
AI agents are key to improving shopping by providing personalized advice. OpenAI’s Operator uses a lot of data to suggest things that match your preferences, which can lead to bigger orders and fewer returns.
Thanks to AI, companies like Amazon have seen a big jump in sales. As more people shop online, keeping up with AI is crucial to stay ahead.
15. AI Agents Examples in E-commerce Platforms
The AI agents behind these systems are Autonomous Learning Agents and Utility-Based Agents. They learn from user data—browsing history, purchase patterns, and product reviews to refine their recommendation models.
By using a utility function, they balance the goal of making more sales with the customer’s desire for relevant and delightful suggestions. This dual approach ensures the suggestions are not just accurate but also delightful to the user, and hence in higher engagement and loyalty.
16. Dynamic Pricing Systems
AI agents enable dynamic pricing by analyzing market trends, demand fluctuations and competitor pricing in real time. This allows businesses to adjust prices automatically and maximize revenue while offering competitive rates.
Retail giants like Amazon and Walmart use AI driven pricing models to optimize sales so customers get the best deals and companies make profits.
AI Agents Examples in Autonomous Vehicles and Robotics
AI agents are the basis of autonomous machines. By combining perception, planning and execution, these agents operate safely in dynamic environments, from highways to warehouses.
22. Autonomous Driving
Self-driving cars have multiple agent layers.
- Perception stacks process lidar, radar, camera, and GPS data in real time.
- Utility-based planning weighs safety, comfort, and efficiency to decide lane changes, merges and emergency maneuvers.
- Execution agents translate plans into steering, acceleration and braking commands.
Companies like Tesla, Waymo and Cruise are pushing these systems with billions of miles and simulated scenarios.
23. Mobile Robots and Drones
Fleet agents coordinate groups of robots or drones for logistics and inspection tasks.
- Coverage planning: Agents allocate routes to ensure complete scanning or delivery coverage.
- Charging optimization: Drones and robots are scheduled to return to charging stations before batteries deplete.
- Collision avoidance: Multi-agent systems share location data and adjust paths in real time to prevent accidents.
These capabilities make mobile agents essential in warehouses, agriculture, and search and rescue.
24. Industrial Robotics
Industrial robots powered by AI agents combine precision with flexibility.
- Task agents perform specialized functions like welding, assembly or quality inspection.
- Supervisor agents monitor overall workflow, enforce safety limits and stop operations when anomalies occur.
- Learning agents adapt to new product designs so flexible manufacturing without reprogramming.
This layered structure increases throughput, reduces downtime and improves worker safety on the factory floor.
Enterprise AI Agents Example: Aisera
While there are many AI agent examples in the artificial intelligence space, Aisera is one of the enterprise agentic AI leaders that solves real business problems at scale. Aisera’s platform uses sophisticated AI agents to automate workflows across IT, HR, sales and customer service. Unlike simple AI solutions, Aisera’s AI agents are designed to understand complex intent, orchestrate multi-step tasks and integrate with existing enterprise systems.
They can do things like automatically resolve IT tickets, onboard new employees, or personalize sales outreach. By combining deep learning, knowledge graphs and multi agent system, Aisera provides a complete solution that not only answers questions but also completes tasks. That’s why it’s an example of how intelligent agents are moving from theory to practice for modern enterprises.
AI Agents in Business Future
Agentic AI companies are transforming many industries very fast. Key areas like autonomy, hyper-personalization, and self-improving systems are leading the way.
Multi-agent systems (MAS) are frameworks of multiple autonomous agents interacting within a shared environment. These can achieve complex goals through the dynamic interactions of relatively simple agents.
– Autonomy
Future AI agents will include agents who make decisions independently more often. For instance, generative AI in business software can create content and help with customer service. This will allow companies to respond faster and keep customers happy.
Technologies like edge computing also play a significant role. They help with tasks that need quick action, like in self-driving cars and smart homes.
– Hyper-Personalization
AI is getting better at personalizing everything. Multimodal AI agents can look at different kinds of data, like medical images and patient records, to help doctors make better diagnoses.
In retail, AI makes shopping more personal and sales go up. AI agents can give personalized financial advice and adapt learning plans to each person.
– Self-Improving Systems
Self-improving AI systems are big. They can find and fix their own problems, less downtime. AI agents use methods like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to make their answers more accurate.
Self-improving is a crucial capability for AI systems in fields such as healthcare and finance. Without constant supervision, AI agents can work better and longer.
As AI agents evolve, businesses must keep up to stay ahead. The examples we’ve seen show the huge potential of AI. From making decisions alone to offering personalized services, AI is changing how we work and live.
These changes can make businesses more efficient and profitable and provide a better customer experience. So embracing these trends is the key to success in today’s fast paced world.
Conclusion
AI agents are changing the way we work today. They can do complex tasks, predict trends, and make things more personal. Moving forward, wise use of AI agents in various industries is key to success for companies. Artificial intelligence agents will lead the way to better businesses, faster and more competitive.
FAQs
What is an example of an AI agent?
What are the 5 types of agents in AI?
- Simple Reflex Agents – React based on predefined rules.
- Model-Based Reflex Agents – Maintain an internal model for decision-making.
- Goal-Based Agents – Plan actions to achieve objectives.
- Utility-Based Agents – Optimize decisions using a utility function.
- Learning Agents – Adapt and improve based on experience.