What is a multilingual AI agent?
A multilingual AI agent is an autonomous self-service system that utilizes Natural Language Processing (NLP), Natural Language Understanding (NLU), and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to grasp intent, maintain context, and execute tasks across multiple languages.
Calling it a tool that can just automatically translate underplays its true capabilities. While legacy systems swap words using basic machine translation, a multilingual AI agent understands the underlying intent. This distinction matters because it allows global companies to serve diverse customer bases without losing the nuance of cultural accuracy. Here is a quick example of the key differences between the two:
- Legacy Machine Translation: Simply swaps “Passwort zurücksetzen” for “Reset password.”
- Multilingual AI Agent: Recognizes the intent to reset the password, verifies the user’s identity via an IAM integration (like Okta), and triggers the reset workflow—all in the customer’s preferred language.

When these multilingual capabilities come together, employees and customers get help that feels natural, regardless of which language they speak or where they’re located.
Why Multilingual AI Matters for the Global Enterprise
In today’s global workplaces, employees often need support that transcends time zones, borders, and languages. Yet many legacy systems still operate solely in English, creating barriers for people whose first languages differ. These persistent gaps show why global organizations are reimagining how they deliver knowledge and assistance. Rather than managing separate help desks or relying on after-the-fact translation, forward-looking enterprises are turning to Language Operations (LangOps), a unified strategy that treats every language as an equal asset in driving collaboration, inclusion, and operational efficiency.
What global companies truly need is “Language Sovereignty”, the ability for an employee to access a knowledge base written in many languages as if it were their own preferred language. By integrating multilingual AI into the support fabric, organizations often see up to an 80% reduction in ticket volume while improving satisfaction across diverse teams and customer bases. This technology removes the communication barriers that once hindered global audiences, ensuring equitable support experiences for everyone—no matter where they live or which language they speak.
How Multilingual AI Works: From Translation to Agentic Reasoning
The evolution from basic translation to intelligent reasoning represents a fundamental shift in Natural Language Processing (NLP).
The Shift from Machine Translation (MT) to LLMs
Traditional machine translation tools operate on statistical rules. They struggle with domain-specific jargon and diverse languages. By contrast, modern machine learning models and Generative AI are trained on billions of service interactions. These AI tools don’t just “swap” words; they reason through them, grounding the response in your company’s specific business logic to ensure cultural accuracy across different languages.
Multilingual RAG and Contextual Reasoning
Modern AI agents use RAG to connect to your enterprise’s data. Aisera takes this further with multi-lingual RAG, allowing the agent to retrieve a solution from a document written in one language and provide the answer in the customer’s preferred language without a separate step.
The “Context Gap” Challenge
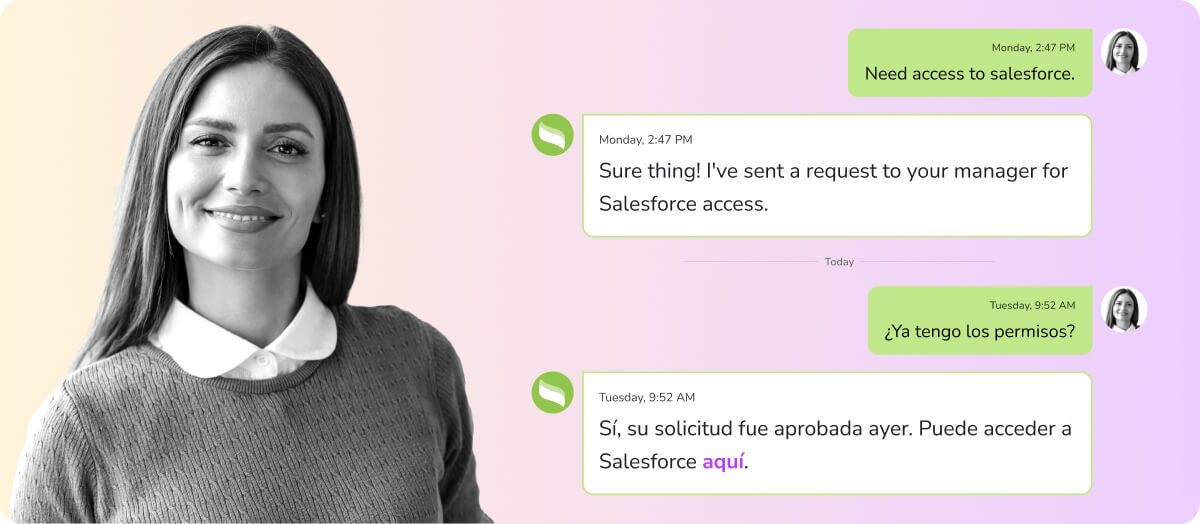
Imagine a user who starts a conversation in English on Monday. On Tuesday, they follow up via a mobile app in their native language (Spanish), simply asking: “¿Ya tengo los permisos?”
- Where legacy systems fall short: A standard system would simply translate the request and ask the user to re-clarify their request, since it has lost the context of previous interactions.
- The Aisera solution: Our multilingual AI agent uses advanced reasoning and natural language processing to connect “los permisos” back to the original request, queries the ITSM, and responds in the user’s native language with real-time status.
Bridging Global Knowledge Silos
AI reasoning capabilities also solve the “siloed knowledge” problem. With Agentic Multilingual AI, your system can ingest knowledge articles (no matter which location they came from) and immediately surface that solution to global audiences in their native languages. For example, if a member from the Japanese IT support team writes an article troubleshooting a clever bug, Aisera can ingest the article and surface the solution to any employee across the globe. This ensures knowledge moves fluidly across global markets.
High-Impact Use Cases for Multilingual AI Agents
- 24/7 Support for Global Businesses: Multilingual AI agents provide instant support for routine requests – no need to wait for support teams to come back online. For example, an employee in Greece can troubleshoot a VPN issue at 3 AM local time in their preferred language and execute the correct process to resolve the issue.
- Real-Time Multilingual Voice Agents: Advanced artificial intelligence now accounts for phonetic and regional accents, reducing the friction often found when human agents or support teams are unavailable.
- Agentic Sales for Global Markets: A multilingual AI agent can act as an asynchronous sales rep, qualifying leads in the customer’s preferred language and handing off all relevant information to human agents with a fully translated conversation history.

5 Technical Benchmarks of a High-Performance Multilingual AI Agent
When evaluating enterprise-grade solutions for multilingual AI agents like Aisera, look beyond surface-level translation. To ensure global scalability and reliability, a platform must meet these five high-performance benchmarks:
1. Ultra-Low Latency (The TTFT Metric)
In a global support environment, “Time to First Token” (TTFT) is a critical performance metric. If a multilingual AI bot has a delay of more than 2 seconds, it creates new points of friction. Use machine learning techniques like Model Quantization and caching strategies to ensure near-instant responses in a diverse range of languages.
2. Native Multi-LLM Orchestration
A top-tier multilingual AI tool should offer Model Agnostic Orchestration, routing queries to the LLM that best handles the nuances of various languages
3. Unified Context
The agent must maintain a unified context across all employee and customer interactions to ensure a seamless experience. For example, whether the user switches from Slack to SMS, the multilingual AI must recognize their identity and previous interactions, regardless of the different languages or mediums used.
4. Deep Agentic Integrations (MCP)
Agents must be able to connect requests to tangible actions in the enterprise. Ensure your multilingual AI supports the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to execute workflows in platforms like ServiceNow or Salesforce directly.
5. Asynchronous Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Controls
For highly sensitive tasks, the AI agent should be able to draft the response and be able to pause for human agents to verify the tone and accuracy.
Final thoughts about multilingual AI
The need for multilingual AI agents highlights how organizations must think about supporting employees, moving from a model that asks people to adapt to systems to ones that adapt to people. With that, organizations can provide consistent, high-quality assistance to everyone in the language they prefer.
Agentic AI is what really makes the shift possible for a global customer base. Rather than relying on simple machine translation, agentic systems use advanced natural language processing to truly understand user intent and take actions autonomously.
Aisera’s platform is purpose-built with multilingual capabilities for 100+ languages, allowing its multilingual AI agents to seamlessly support workforces across global markets. By integrating AI that respects the preferred language of every user, organizations can deliver frictionless support from end-to-end. Book a demo today to see how we help global businesses overcome language barriers. Book an AI demo to see Aisera’s system of AI agents in action.