AI Workflow Automation
Automate complex requests to empower self-service, boost productivity and cut costs
Enhance operational efficiency with AI workflow builder. Aisera’s AI workflow automation engine uses Agentic AI reasoning and orchestration to autonomously execute intelligent workflows, automating complex user requests and seamlessly integrating human and machine tasks into an end-to-end flow. It extends beyond single-task automation, encompassing entire business processes and interactions across multiple applications, ultimately reducing resolution times, and boosting user satisfaction.
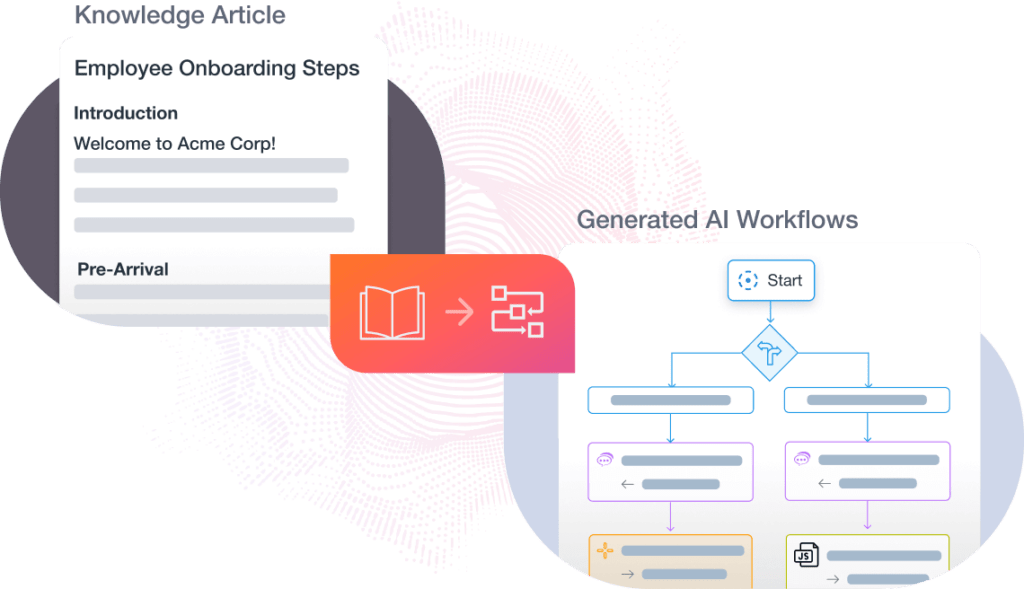
Generate AI Workflows
Leverage automated processes to ingest, parse, and process knowledge base articles while evaluating their suitability as a zero-shot (as-is) or conversation flow, where the KB articles are converted into AI workflows based on organization and content.
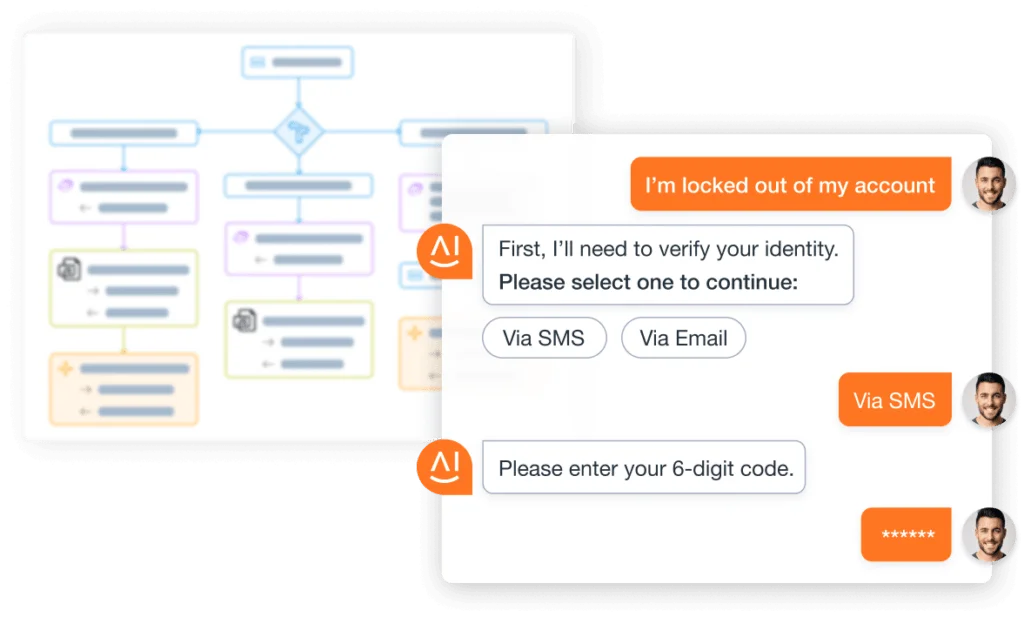
Third-Party Workflow Execution
Eliminate the need to re-create AI workflows and decrease development time by seamlessly importing existing workflows or by triggering them from 3rd party systems like UiPath, Workato, ServiceNow, and more.

LLM-Powered AI Workflow Library
Utilize 3,000+ pre-built and third-party LLM-powered AI workflows to auto-remediate requests and minimize the need for human intervention. AiseraGPT AI workflows can be triggered conversationally through system events, webhooks, schedules, and event data posted from other systems.
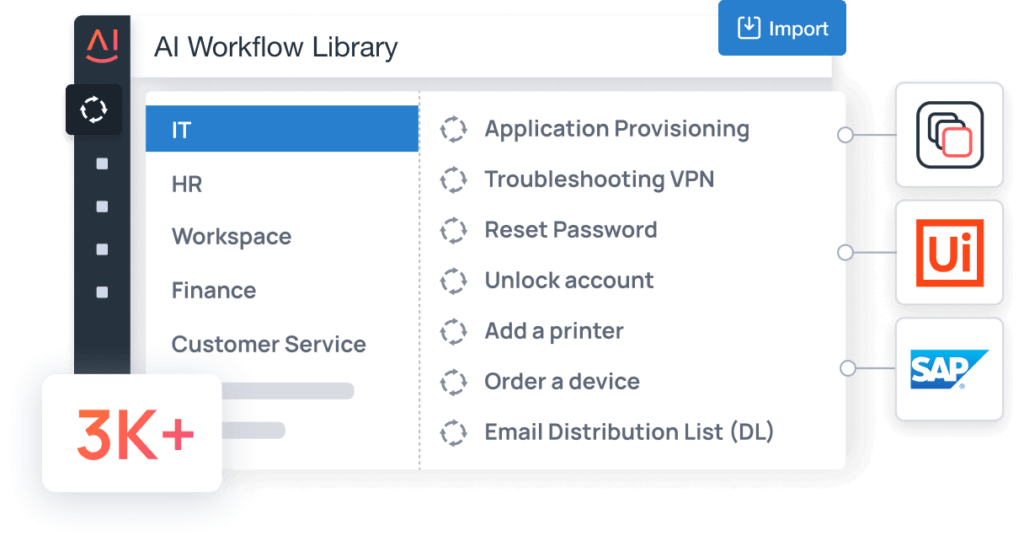
Rich, Pre-Built Integrations
Maximize the automation of complex employee requests across business services and applications with 500+ back-end connectors using open APIs. Seamlessly connect with your existing tech stack such as ServiceNow, Salesforce, Workday, Nexthink, Okta, Microsoft Teams, Slack, and more.

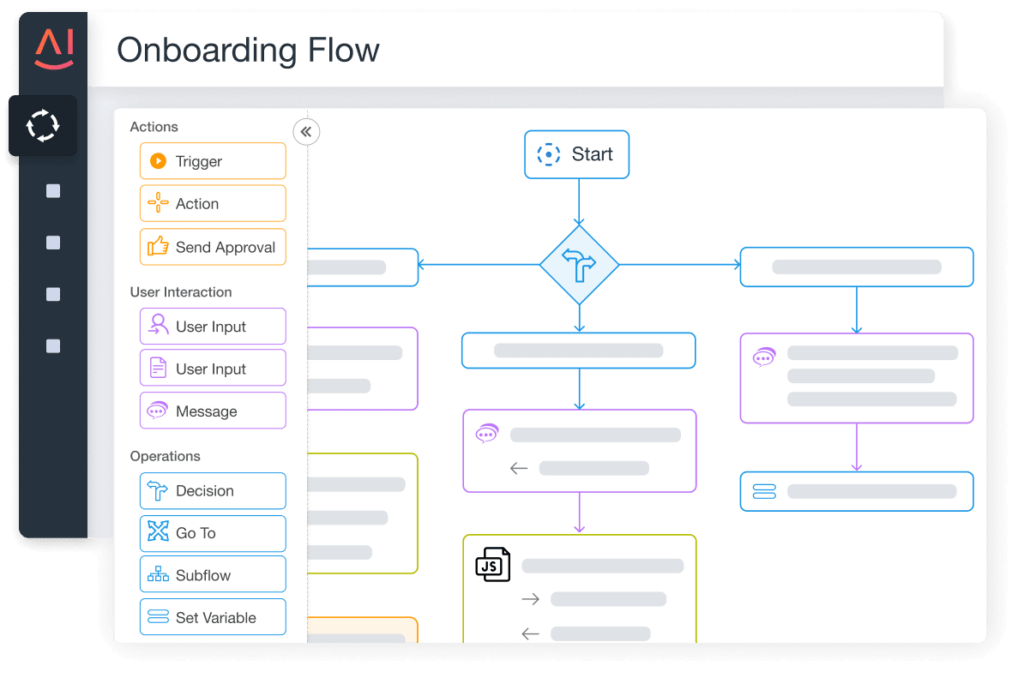
Low-Code/No-Code Visual Studio
With Aisera’s Low-Code/No-Code studio, you can build automations with a drag-and-drop interface and orchestrate tasks and actions across multiple applications. Users can also leverage Aisera’s pre-built workflow library for turnkey automation.
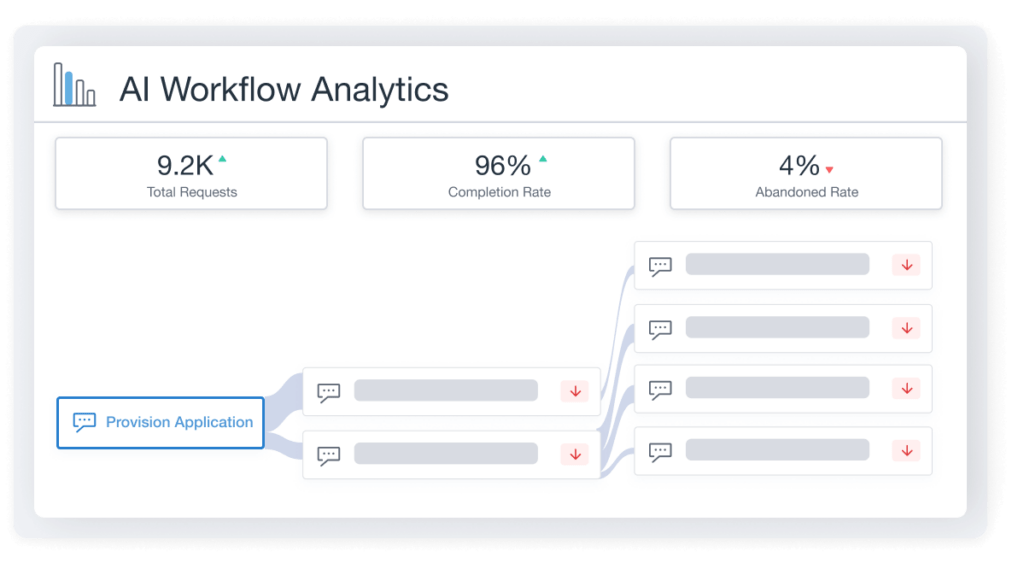
Key Insights into Workflow Analytics
Aisera provides detailed analytics that give visibility into service gaps and common user behaviors. Identify bottlenecks and pinpoint where drop-offs are occurring while auto-streamlining workflows over time with Aisera’s comprehensive insights dashboard and reports.
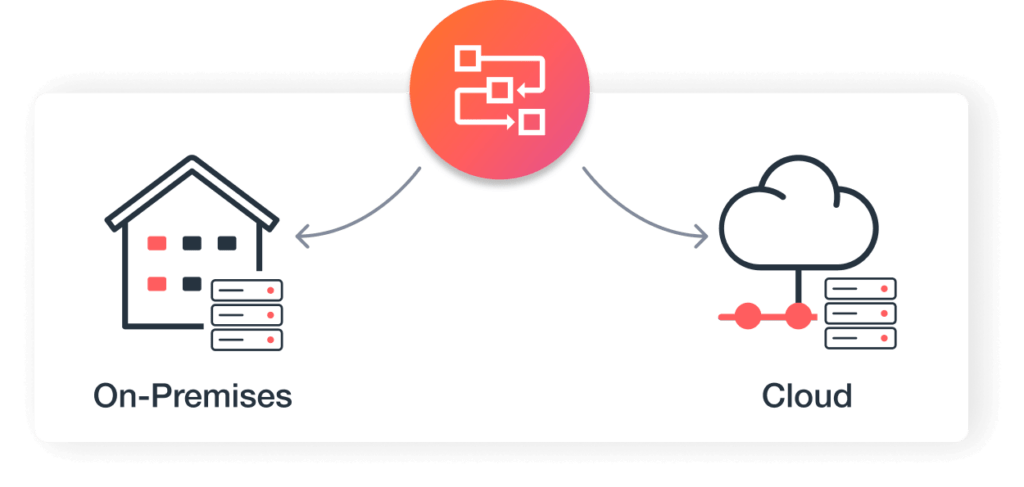
On-Premises and Cloud Execution of Workflows
Deploy workflows and automations that span cloud-only, on-premises remote workflows only, or a hybrid of cloud and on-premises applications that work for a variety of environments.