Introduction to AI Agents vs Agentic AI
Agentic AI vs. AI agents, yes, there’s a difference. While many people use these terms interchangeably, they represent related but distinct concepts. Agentic AI and AI agents are similar, yet provide different value to organizations.
When most people think of artificial intelligence, they think of Generative AI. Think ChatGPT or Claude: you provide a prompt, and the GenAI generates an intelligent output based on that prompt.
Agentic AI is a fundamentally different approach. It emphasizes autonomous agents action and goal-directed behavior, orchestrating systems that are designed to perceive the environment, make autonomous decisions, plan actions, and work toward specific objectives with minimal human intervention.
To better understand agentic AI, let’s first look at its “building blocks”, AI agents, then look at how an agentic AI platform deploys agents to accomplish its stated objectives. In this blog, we’ll walk through the nuances of each, how they’re interrelated, and some real-world examples to show the power of Agentic AI and how it’s the next step in AI evolution.
What is an AI agent?
AI agents are autonomous software programs that independently execute tasks via machine learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and large language models (LLMs). The best use cases for AI agents include providing automated answers to key queries, deploying predefined workflows and task sequences, engaging in predictive analysis and alerts, and more.
Key benefits of AI agents include:
- Better productivity and efficiency by automating repetitive, time-consuming tasks
- Cost reduction and improved ROI by reducing dependency on manual work
- More seamless customer experiences due to instant, personalized, and comprehensive responses to queries
What is Agentic AI?
Unlike AI agents, Agentic AI refers to the overall concept of artificial intelligence systems that can act independently and achieve goals, and AI agents are the individual components within the system that execute tasks. Agentic AI orchestrates not only traditional AI agents, but also other systems and even human actions to plan, decide, and execute multi-step workflows to achieve specific goals. Agentic AI acts autonomously, adapts in real time, and initiates tasks while learning continuously from feedback.
The four most common types of AI agents used in agentic AI are generative information retrieval agents, prescriptive knowledge agents, dynamic workflow agents, and user assistant agents.
Agentic AI operates with minimal human intervention, determining specific courses of action to best achieve pre-determined solutions, i.e., stated business outcomes. Additionally, agentic AI can integrate and orchestrate enterprise systems to automate complex, multi-system agentic workflows in real time, like autonomous customer support resolution, fraud detection, financial planning, and more.
From AI Agents to Agentic AI: The Evolution
AI agents and agentic AI represent two stages along AI’s evolutionary path. The earliest AI efforts were simple: create programs to mimic human decision-making within limited contexts. Through the rest of the 20th century, AI began to acquire human agent-like qualities, but still had limited autonomy.
Everything started to change in the 21st century when machine learning (ML), neural networks, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and reinforcement learning (RL) emerged as viable technologies. These technologies can learn from existing data, adapt to change, and pursue goals with minimal human oversight. Multi-agent systems (MASs) enable further collaboration among existing models.
AI agents operate without excessive human intervention. They can plan several steps and excel at completing the specific tasks for which they are designed. Some agents, such as task agents that book meetings, approve expenses, and more, excel in structured tasks, while domain agents are designed to handle broader, more unstructured requests like answering a variety of IT & HR requests.
Agentic AI represents the next evolution of AI– an overarching paradigm of combining the capabilities of AI agents to operate independently and collaborate with multiple interconnected systems and agents.
Discover Aisera’s system of AI Agents in this quick demo video. See how these intelligent systems streamline operations and enhance user experiences with advanced automation
AI Agents vs Agentic AI Key Characteristics Comparison
AI Agents: Functional Traits
Because AI agents can operate intelligently within their designated environments, they perform even more advanced functions than traditional AI and automated systems.
- Goal-directed behavior that can execute independently without constant human supervision
- Gathering and interpreting information within the environment using sensors or digital interfaces
- Assessing changes within the controlled environment and responding—enabling adaptive behavior based on new information or evolving conditions (but only within the environment)
- Ability to learn from experience and improve performance over time
Agentic AI: Core Abilities
Agentic AI embodies a higher-order coordination and reasoning layer where AI agents are components that it orchestrates. These systems excel at tackling more complex tasks, multi-step challenges, coordinating across domains, and adapting their strategies as new information emerges.
The core abilities of agentic AI systems include:
- Higher autonomy and the ability to make complex decisions without human involvement
Continuous learning and the ability to adapt to feedback in real-time or near real-time
- Ability to predict and evaluate potential outcomes to determine the best course of action
- Proactivity in identifying potential issues, initiating solutions, and optimizing processes, without human prompting.
- Collaboration, coordination, and orchestration of different AI agents, enterprise software systems, and human users
Fundamental Differences Between Agentic AI and AI Agents
1. Autonomy and Control
AI agents work well at planning and performing specific tasks within their domain and skillset. For example, an IT domain agent is an expert in all things IT, including detecting incidents, answering IT questions, and resolving service requests.
Agentic AI is the higher-level paradigm of interpreting goals, breaking them down into steps, and coordinating multiple agents and systems to get the job done. If you’re using AI agents exclusively, you lose this orchestration layer, meaning you’ll need to manually coordinate agents to complete complex, multi-step objectives.
2. Complexity of Tasks
Most organizations already have a robust tech stack to handle structured and straightforward tasks: retrieving information from knowledge bases, generating reports, booking meeting rooms, and more. While individual AI agents can make these well-defined, complex tasks more efficient and less reliant on manual effort, they need a higher level of orchestration to achieve bigger and better things.
The agentic AI approach is focused on providing that orchestration. An agentic AI system interprets complex scenarios, breaks them into steps, and coordinates the appropriate AI agents and systems to solve the problem. Implementations based on this approach can reduce operational time, conserve resources, and also enable scalable solutions that adapt dynamically without requiring heavy manual coordination or excessive costs.
3. Learning and Adaptation
Typical enterprise AI agents can plan and adapt in their specific tasks and domains, but they still need explicit training and fine-tuning to perform effectively and expand their capabilities. Expanding an AI agent’s capabilities often means devoting time and resources to retraining and updating the model, as the AI agents learn and improve primarily by focusing on well-defined workflows and domain-specific problems.
Agentic AI takes a broader, system-level approach that connects and coordinates multiple AI agents working collaboratively across domains. It continuously learns from experience and feedback across the entire system, allowing it to interpret new data, dynamically adjust strategies, and refine its approach without needing explicit retraining for each change.
This continuous, adaptive orchestration makes Agentic AI well-suited to managing complex, evolving environments with greater scalability, efficiency, and reduced manual intervention.
4. Depth of Decision-Making Processes
From customer support to HR, finance, and beyond, AI is being used to handle increasingly complex and varied challenges across the organization. In this environment, no single solution fits every situation, and it’s impossible to anticipate every possible issue.
Agentic AI uses advanced AI reasoning and chain-of-thought planning, autonomously evaluating different factors and their possible outcomes and adapting to new situations without requiring constant human handholding. This allows the system to make strategic decisions in changing scenarios.
AI agents also leverage contextual understanding and adaptive decision-making powered by advanced AI models. They can execute multi-step workflows and leverage integrations to enterprise systems, but their decision-making scope is typically focused on clearly defined goals or domains. They may rely on additional human input or escalation when handling ambiguous challenges.
5. Environmental Awareness
Every organization has its own unique procedures, policies, workflows, and even terminology. Delivering exceptional employee experience requires AI that can operate beyond silos and adapt to a diverse enterprise environment with contextual intelligence.
AI agents bring targeted environmental awareness to their respective domains.
For example, an IT agent automates incident ticket routing by leveraging incoming data from monitoring tools and recognizing patterns in historical data. These agents adapt to contextual information relevant to their scope but typically focus on domain-specific, goal-oriented challenges.
Agentic AI applies a slightly different approach to sustain broader and deeper environmental awareness, drawing on insights across its system of agents to make coordinated decisions in dynamic, open-ended environments.
For example, an agentic AI system managing a company-wide outage would coordinate IT response by executing the appropriate runbook and providing employee communications while updating its plan in real-time as conditions change.
By coordinating multiple AI agents with this adaptive approach, organizations get the accuracy of domain-specific expertise and increased flexibility, allowing them to operate faster and more intelligently.
6. Integration and Orchestration
The average tech stack size for an enterprise organization is 664 applications. When you consider all that goes into managing these tools—licenses, credentials, data sharing, integrations, security, and compliance—it’s too much for a human (or even a team of humans) to handle manually.
However, failure to fix a fractured tech stack is equally costly. On average, organizations lose 38% of their revenue from broken integrations. When it comes to improving employee experiences, 85% of HR leaders feel the pressure to consolidate their tech stacks.
While AI agents deliver powerful, domain-specific knowledge and automation by integrating with specific systems or workflows, their capabilities are typically confined to single platforms or functional areas.
For example, an IT agent can automate ticket routing within an ITSM tool like ServiceNow or Jira, while an HR agent can handle payroll questions within a payroll system like Workday or Rippling. The point is, these agents excel at focused tasks by leveraging the relevant data and APIs within their scope.
With an agentic AI system, it coordinates multiple AI agents and systems, finding the right agent for each task and synthesizing information across domains (IT, HR, Finance, and more) to provide a holistic solution that enhances productivity and overall employee experience (more on that below).
Real-World Agentic AI Use Cases
Let’s take a look at some real-world use cases to show how organizations are using agentic AI to improve their employee experience.
Autonomous IT Support and Technology Orchestration
As mentioned above, enterprise tech stacks and IT infrastructures are large, expansive, and unwieldy for the average user. Add on top of that the necessary network security and verification layers, and the average employee has to jump through multiple hoops just to update their password, configure their VPN, request software access, or retrieve files from a secure server.
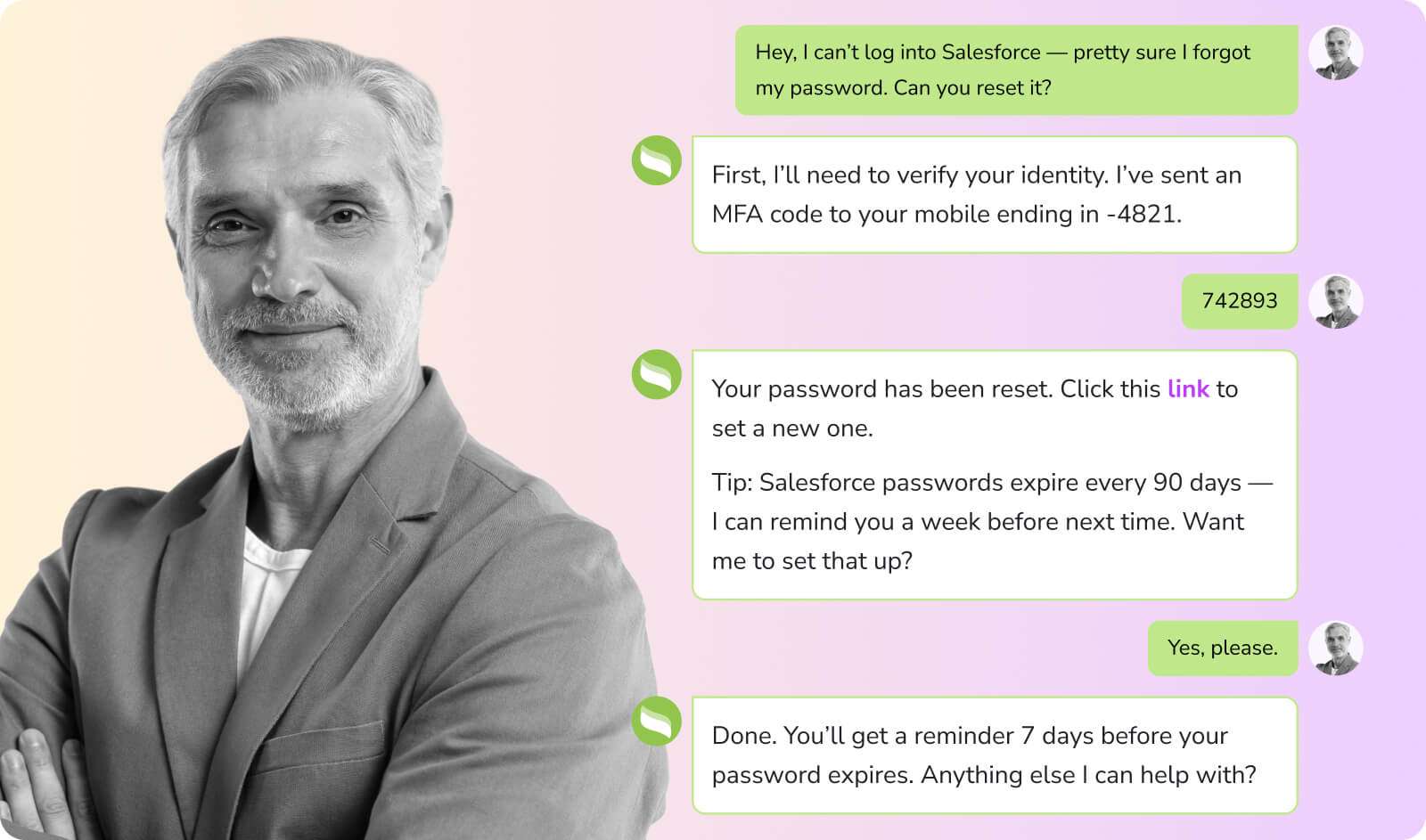
When an employee is navigating an IT issue and has a question, they can simply query the company’s agentic AI system, which will then:
- Clarify any questions (if necessary)
- Autonomously orchestrate the various platforms to resolve the issue (e.g., password reset, recording access)
- Provide the employee with best practices to better navigate the issue in the future
The result? Faster ticket resolution, which improves overall productivity and enables your IT team to devote more time to high-value work.
Personalized Onboarding and Training
New employees start their journey at a new company in different ways. Some might arrive with a long list of questions on day one. Others bring up questions gradually as they progress through onboarding, and many fall somewhere in between.

Delivering an impactful onboarding experience means accommodating these different learning styles to ensure that everyone can ramp up and be engaged as quickly as possible.
We’ve seen our clients use agentic AI to accelerate the onboarding process by providing new employees with a personalized assistant that guides them through key questions with real-time data. By equipping new hires with an intelligent, always-on AI agent that walks them through processes and guides them to relevant resources, our clients enhance their onboarding experience without needing to increase headcount or administrative effort.
Real-Time Benefits Management
When employees engage with HR, they often end up spending a significant amount of time navigating multiple platforms just to perform a simple task. For example, a task as simple as increasing 401(k) contribution by 1% can easily turn into an hour-long exercise. (And that’s not including the time it takes to remember that special password you created for your investment account that you only log into once every few months!)

We’ve seen our customers deploy Agentic AI to not only answer key HR questions but also take actions across various backend platforms. In the example agent above, employees can simply request the change to their contribution amount, and our agentic AI system coordinates the necessary updates behind the scenes, completing the request quickly without needing to pull in a human agent.
Benefits and Challenges of Agentic AI Systems
| Benefits | Challenges |
| Higher levels of organizational efficiency and productivity | Ensuring transparency and explainability for all Agentic AI decisions and the reasoning behind them—no “black boxes” |
| Scalable employee management with limited cost increases | Data accuracy, comprehensiveness, and privacy |
| Coordinated decision-making across domains | Bias inherited from training data can inadvertently lead to inequitable outcomes |
| Employee support that adapts to individual needs and evolving situations—especially when domain-specific agents are deployed | Need for clear escalation paths and clear standards for when human intervention is needed |
| Improved security and compliance by reducing human error, especially when accessing sensitive systems | Complex implementation that requires technical and contextual knowledge |
Conclusion: The Future of Intelligent Systems
Think back to that brief history of AI agents vs. Agentic AI from above. The shift into the adaptive, cross-domain intelligence of Agentic AI is only moving faster, going beyond singular use cases towards shaping the entire employee experience.
Organizations that move quickly stand to reap the benefits quickly – lower costs, higher productivity, and increased operational efficiency. But implementing agentic AI delivers something even more valuable – a forward-facing foundation that adapts to changing conditions and continues delivering value as intelligent systems evolve. Start now to capture both the immediate rewards and ensure that your enterprise is ready for whatever comes next in intelligent systems.
To learn more about how Agentic AI helps to improve the employee experience, book a free AI demo.


